Blockchain in Supply Chain Transparency: The Future of Global Logistics
Why Blockchain Is the Future of Supply Chain Transparency
In today’s interconnected economy, blockchain in supply chain transparency has emerged as a transformative force reshaping how businesses manage logistics, compliance, and trust. With global supply chains spanning continents and involving numerous intermediaries, visibility and authenticity have become critical challenges. Traditional systems often lack accountability, leaving room for inefficiency, fraud, and misinformation.
Blockchain, a distributed ledger technology, is now offering a breakthrough — one that provides immutable record-keeping, real-time visibility, and data integrity across every step of the supply chain. As enterprises race to digitize operations, blockchain stands at the center of this evolution, enabling businesses to trace products, verify authenticity, and foster trust between partners and consumers.
Understanding Blockchain in Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain is not just about cryptocurrency — it’s a digital trust architecture. In supply chain management, it records transactions securely and transparently, ensuring all stakeholders share a single, tamper-proof version of the truth.
When a product moves from manufacturer to distributor, each transaction is digitally signed, timestamped, and stored in a decentralized ledger accessible to all authorized participants. This creates a shared system where no single entity can alter records without detection.
How Blockchain Enhances Supply Chain Transparency
- Immutable Records: Each transaction is permanent, creating a verifiable audit trail.
- Decentralized Validation: Eliminates the need for intermediaries by verifying data across the network.
- Real-Time Visibility: All participants can see the same data instantly.
- Improved Traceability: Products can be tracked from origin to consumer.
- Enhanced Accountability: Every change is tied to a verified participant.
Through this combination of transparency and trust, blockchain helps supply chains operate with unprecedented clarity and efficiency.
The Key Role of Blockchain in Supply Chain Transparency
End-to-End Product Traceability
Consumers today want to know where their products come from, whether their coffee is ethically sourced or if their electronics are manufactured sustainably. Blockchain enables this by documenting every step — from raw material extraction to final delivery.
For instance, IBM’s Food Trust blockchain allows retailers like Walmart to trace food items back to their farm origin in seconds. Previously, tracing contaminated food took over a week. Now, it takes 2.2 seconds — drastically reducing waste, fraud, and health risks.
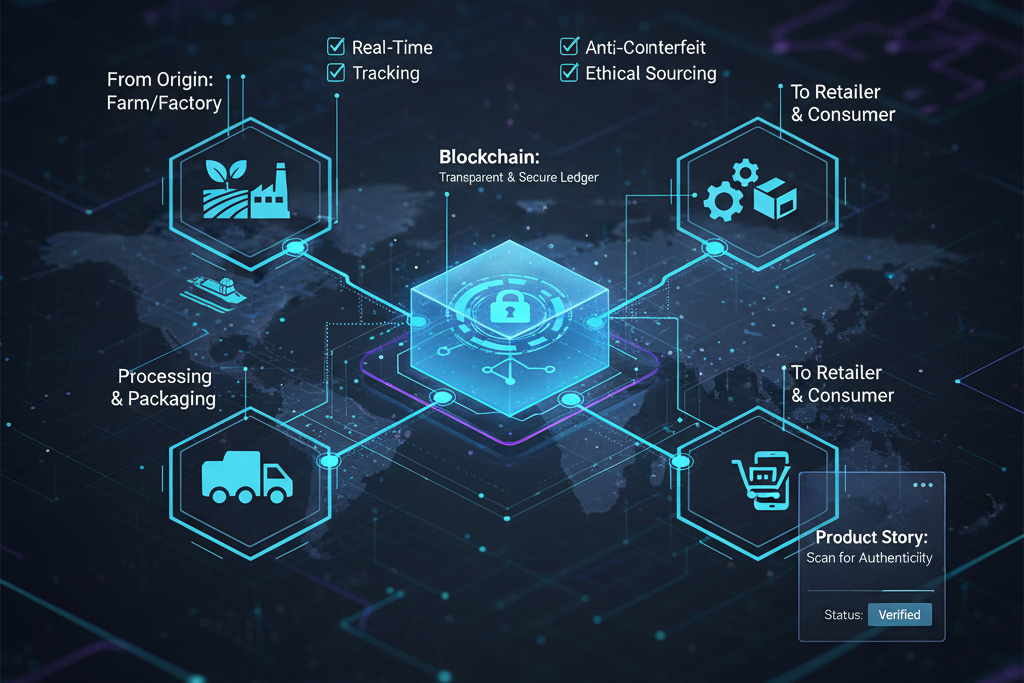
Authenticity Verification and Anti-Counterfeiting
Counterfeit goods cost the global economy over $500 billion annually. Blockchain combats this by issuing unique digital identities for every product. These identities can’t be replicated or forged, ensuring authenticity at every stage of the supply chain.
Luxury brands such as LVMH and De Beers use blockchain to verify product origins. De Beers, for example, tracks each diamond’s journey from mine to retail, certifying that it’s ethically sourced and conflict-free.
Supplier Accountability and Ethical Sourcing
Modern supply chains depend on numerous suppliers, making verification complex. Blockchain streamlines this by storing supplier credentials — certifications, environmental compliance, and labor standards — on a transparent ledger.
Businesses can quickly verify suppliers’ ethical practices, ensuring compliance with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) goals. This transparency strengthens brand reputation and ensures fair trade across industries.
Real-Time Inventory and Logistics Tracking
Blockchain integrated with IoT sensors provides live updates on shipments — temperature, location, humidity, and more. When combined with smart contracts, the system can automatically trigger alerts or payments when specific conditions are being met.
For example, Maersk and IBM’s TradeLens platform connects shippers, ports, and customs authorities, reducing documentation errors and saving billions in logistics costs annually.
Business Benefits of Blockchain-Enabled Transparency
1. Enhanced Efficiency and Cost Reduction
Automating manual verification and documentation processes saves time and eliminates duplication. According to Deloitte, blockchain can reduce supply chain administrative costs by up to 50%.
2. Fraud Prevention and Security
Each transaction on the blockchain is encrypted and verified, by preventing data manipulation. Fraud detection becomes instantaneous since every party views the same unalterable data.
3. Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
Blockchain simplifies compliance by creating immutable audit trails. For industries like pharmaceuticals and food, this is crucial for meeting FDA, ISO, and other international standards.
4. Improved Customer Trust
Transparency breeds trust. When customers can trace products and verify authenticity, they are more likely to engage and remain loyal.
5. Sustainability and Ethical Impact
By tracking emissions, sourcing, and supplier practices, companies can report sustainability data confidently — a growing demand among consumers and investors alike.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Supply Chain Transparency
Food and Agriculture
Companies like Nestlé and Carrefour use blockchain to monitor food safety and origin. Blockchain ensures that farm-to-table journeys are being recorded with complete accuracy, reducing contamination risks and enhancing consumer confidence.
Pharmaceuticals
The MediLedger Project ensures drug authenticity and prevents counterfeit medications by tracking every movement in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
Automotive Industry
Manufacturers like BMW track component origins to ensure ethical sourcing of raw materials such as cobalt used in electric vehicle batteries.
Fashion and Luxury Goods
Brands like Prada and LVMH use blockchain to authenticate luxury goods and fight counterfeiting.
Energy and Commodities
Blockchain tracks carbon credits and renewable energy certificates, enhancing transparency in sustainability initiatives.
How Blockchain in Supply Chain Transparency Works
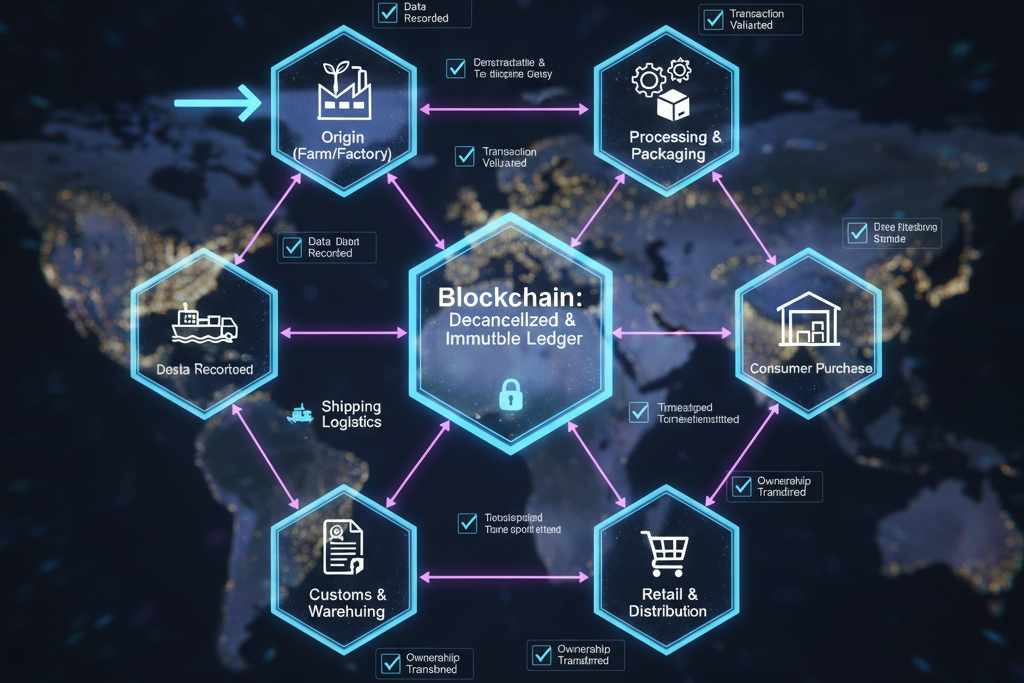
- Recording Events: Each movement or transaction (e.g., production, shipment) is being recorded on the blockchain.
- Verification: Participants validate each entry using consensus algorithms.
- Storage: Verified data becomes permanent, timestamped, and traceable.
- Access: Authorized users view real-time information from any point in the chain.
- Automation: Smart contracts execute actions automatically when predefined conditions are met.
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Blockchain Transparency
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Data Integration | Legacy systems often lack compatibility | Use API-driven middleware for smooth data sync |
| Scalability | Handling large volumes of transactions | Adopt hybrid blockchain models |
| Adoption Resistance | Stakeholders fear transparency exposure | Educate with pilot programs showing ROI |
| Regulatory Ambiguity | Blockchain laws vary across regions | Partner with legal and compliance experts |
| Cost and Complexity | High initial investment | Start with modular solutions and scale gradually |
Steps to Implement Blockchain in Supply Chain Operations
- Identify Transparency Gaps: Determine which processes lack visibility or trust.
- Select the Right Platform: Choose enterprise-grade solutions like Hyperledger Fabric, Ethereum, or IBM Blockchain.
- Start with a Pilot Project: Focus on one use case — product traceability, document verification, or supplier transparency.
- Integrate IoT and Smart Contracts: Enable automated data capture and event-triggered actions.
- Train and Align Stakeholders: Educate all participants about blockchain’s benefits and usage.
- Scale Securely: Gradually expand implementation across suppliers, distributors, and logistics networks.
The Future of Blockchain in Supply Chain Transparency
The next decade will see blockchain integration becoming standard in global logistics. With emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and predictive analytics, blockchain will evolve from passive tracking to proactive decision-making.
Future trends include:
- Interoperable Blockchain Networks connecting industries seamlessly.
- Tokenization of Assets for transparent trading of supply chain commodities.
- AI-Powered Predictive Supply Chains that forecast disruptions in real-time.
- Green Blockchain Initiatives for sustainable logistics tracking.
Call to Action — Build Transparent, Trusted Supply Chains with Tiso Studio
Empower your business with blockchain transparency today.
Tiso Studio specializes in custom blockchain integration for businesses seeking trust, efficiency, and accountability in their operations. Whether you aim to track product provenance, prevent counterfeiting, or improve vendor collaboration — we’ll design a blockchain solution tailored to your industry.
Let’s future-proof your supply chain with blockchain innovation.
Visit our Emerging Technology Services and collaborate with Tiso Studio to unlock end-to-end supply chain visibility.
FAQ’S
1. How does blockchain prevent fraud and manipulation in the supply chain?
Blockchain uses immutable records, meaning once data is added, it cannot be altered or deleted. Every transaction is timestamped, verified, and stored transparently — eliminating data tampering, document forgery, and unauthorized changes.
2. Can blockchain track counterfeit goods and verify product authenticity?
Yes. Each product can be assigned a unique digital identity on the blockchain. This identity follows the product through every stage — from factory to consumer — making it impossible for counterfeit goods to enter or replace the original in the chain.
3. Do companies need to overhaul their entire system to implement blockchain?
No. Blockchain can be integrated gradually using API middleware, allowing businesses to connect legacy systems without disruption. Most businesses start with a pilot use case before scaling.
4. How does blockchain support sustainability and ethical sourcing?
By recording supplier practices, certifications, and ESG compliance on a shared ledger, blockchain ensures accountability. It verifies whether raw materials are sourced responsibly and whether vendors meet ethical and environmental standards.
5. What industries stand to benefit the most from blockchain-enabled transparency?
Industries with complex logistics or regulatory requirements — including food, pharmaceuticals, automotive, fashion/luxury, and energy — gain the most from blockchain due to its real-time traceability, anti-counterfeit capability, and compliance tracking.






Recent Comments