Blockchain for Businesses: Beyond Cryptocurrency
Blockchain for Business: How Blockchain Transforms Modern Enterprises
Most business leaders hear “blockchain” and immediately think of Bitcoin, but blockchain for business offers far more practical applications than cryptocurrency. Designed for executives and decision-makers, this guide explains how blockchain can address real operational challenges — from fraud reduction to supply chain visibility and contract automation.
Companies across industries are now using blockchain to enhance transparency, cut costs, and build trust. Whether you’re in manufacturing, retail, logistics, or finance, blockchain’s secure record-keeping systems can redefine how you manage transactions and relationships.
Understanding Blockchain for Business Applications
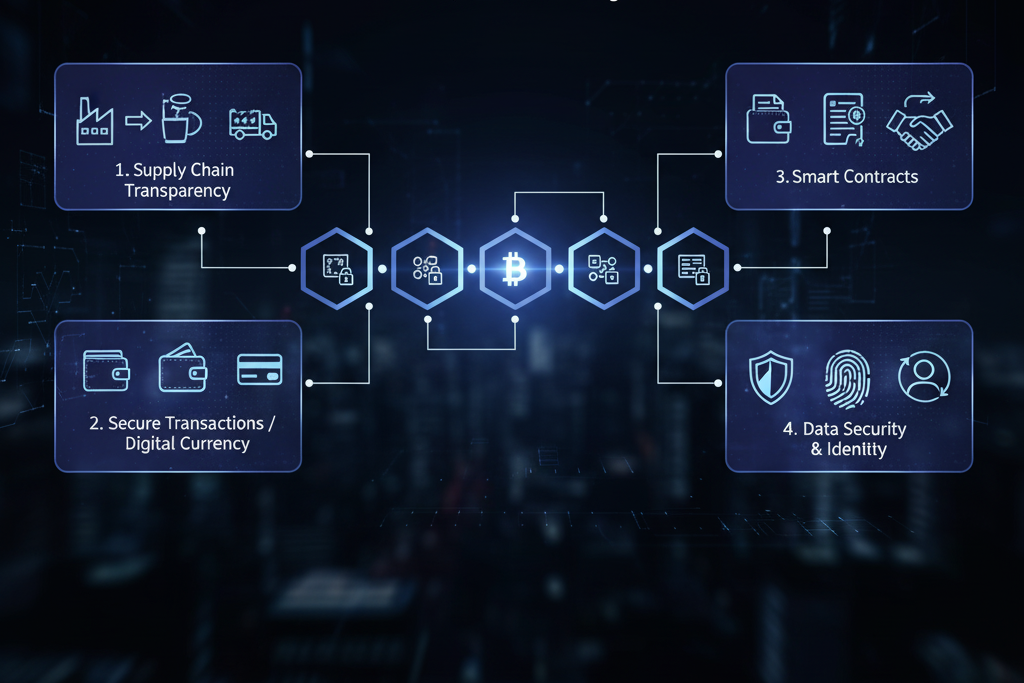
Core Components That Drive Blockchain for Business Value
Blockchain operates through four critical components that generate business value — the distributed ledger, cryptographic hashing, consensus mechanisms, and smart contracts. Together, they create a secure, decentralized system where transactions are verifiable and tamper-proof.
These components help enterprises reduce fraud, eliminate intermediaries, and ensure consistent compliance without manual oversight.
Key Differences Between Blockchain for Business and Traditional Databases
Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain for business uses distributed ledgers maintained across multiple nodes. This removes single points of failure and creates a shared source of truth. Data modification is impossible without consensus, ensuring absolute data integrity and traceability.
| Traditional Database | Blockchain |
|---|---|
| Centralized control | Distributed network |
| Administrator access required | Cryptographic verification |
| Single point of failure | Multiple copies |
| Reversible transactions | Immutable records |
This immutability and transparency make blockchain ideal for industries where trust and verification matter most — such as logistics, healthcare, and finance.
Security and Transparency Benefits of Blockchain for Business
Building a New Model for Trust
Blockchain security relies on encryption and consensus. Each transaction is validated by network participants, reducing dependency on a single administrator. Businesses gain built-in fraud protection and verifiable records for compliance and auditing.
Public blockchains offer complete transparency, while private and consortium versions allow permission-based access — balancing openness with confidentiality.
Compliance Made Simple
Every blockchain entry includes timestamps and digital signatures, creating a verifiable audit trail. This makes regulatory compliance easier for industries that must demonstrate data integrity — such as finance, insurance, and healthcare.
Supply Chain Management Revolution Through Blockchain
Real-Time Product Traceability and Authentication
Blockchain in supply chain management enables real-time tracking of goods from origin to delivery. Using QR codes and RFID tags, manufacturers and distributors update blockchain records at every checkpoint, providing instant product histories.
Companies like Walmart and Maersk already use blockchain for traceability — reducing the time to verify product origins from weeks to seconds.
(Outbound link suggestion: Walmart’s Blockchain Food Safety Initiative)
Reducing Counterfeiting and Fraud
Luxury and pharmaceutical industries lose billions to counterfeit products each year. Blockchain gives every genuine item a unique cryptographic identity, making imitation impossible. Brands like LVMH use blockchain certificates of authenticity to safeguard product legitimacy.
(Outbound link suggestion: LVMH’s Aura Blockchain Consortium)
Streamlining Vendor and Supplier Verification
Supplier verification becomes faster through blockchain. Once verified, supplier data — certifications, compliance records, and performance ratings — becomes permanently accessible on the blockchain. This shared verification system accelerates procurement and improves trust.
Smart Contracts: Automating Business Processes
Automated Contract Execution
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements stored on the blockchain that trigger actions when conditions are met. For example, payments automatically process once goods are delivered. This automation removes intermediaries, reduces administrative costs, and eliminates payment delays.
Reducing Costs and Human Error
Industries such as insurance, real estate, and trade finance use smart contracts to automate claims, escrow, and settlements. Blockchain for business replaces manual paperwork with code-based execution, minimizing disputes and errors.
(Outbound link suggestion: IBM Smart Contract Applications)
Ensuring Compliance
Smart contracts can automatically enforce regulatory requirements — from tax calculation to data privacy compliance — ensuring businesses meet global standards with minimal intervention.
Blockchain-Enabled Digital Identity and Data Management
Secure Digital Identities
Blockchain gives users control over their digital identities through cryptographic keys. Customers can verify their identity once and share that verified record across multiple services securely — a process far more efficient than traditional KYC systems.
(Outbound link suggestion: World Economic Forum on Blockchain Identity)
Data Security and Privacy
Unlike centralized storage, blockchain distributes encrypted data across the network, reducing hack risk. This model protects sensitive business and customer information while ensuring compliance with data protection laws like GDPR.
Financial Services Transformation Through Blockchain
Trade Finance & Global Payments
Blockchain for business has revolutionized trade finance. Smart contracts simplify letter-of-credit processing and cross-border payments. Major institutions like HSBC and JPMorgan now use blockchain platforms to cut transaction times from days to hours.
(Outbound link suggestion: J.P. Morgan’s Onyx Blockchain Platform)
Insurance Claims and Risk Management
Blockchain automates insurance claims through verified triggers like flight data or weather updates. This reduces fraud and shortens processing time dramatically — from weeks to minutes.
Implementing Blockchain for Business Success
Assessing Organizational Readiness
Before adoption, companies must identify operations where blockchain provides measurable value — such as multi-party workflows, audit-intensive processes, or data-sharing between untrusted entities.
Choosing the Right Platform
For enterprise use, platforms like Hyperledger Fabric, R3 Corda, and IBM Blockchain provide permissioned, secure, and scalable environments. Choose based on transaction volume, data privacy needs, and integration compatibility.
Managing Change and Employee Training
Successful implementation requires employee education and leadership buy-in. Create internal “blockchain champions,” provide sandbox environments for testing, and offer continuous training to ease the transition.
Measuring ROI
Measure both quantitative and qualitative results — such as cost savings, fraud reduction, audit efficiency, and improved partner trust. Over time, blockchain enhances business reputation and resilience through proven transparency.
The Future of Blockchain for Business
By 2025, blockchain for business will move from experimentation to full-scale enterprise adoption. As integration with IoT, AI, and cloud computing matures, blockchain will form the backbone of digital transformation strategies across industries.
Future-Proof Your Business with Blockchain Innovation
Ready to make your business smarter, faster, and more transparent?
Tiso Studio helps forward-thinking organizations design blockchain strategies that drive measurable results — from supply chain visibility to smart contract automation.
Visit Tiso Studio’s Emerging Technology Hub to explore more insights on blockchain, AI, IoT, and future-ready digital solutions.
FAQ’S
1. How is blockchain different from traditional enterprise security systems?
Traditional systems secure data through perimeter defenses (firewalls, admin access, etc.), which still creates a single attack point. Blockchain protects data at the record level using cryptography and decentralization — making it nearly impossible to alter or hack without network consensus.
2. Which industries benefit the most from blockchain beyond finance?
Blockchain is now widely used in supply chain, manufacturing, healthcare, retail, energy, logistics, and even government records. Any industry involving audits, traceability, or multi-party workflows gains massive efficiency from blockchain.
3. How expensive is blockchain implementation for an enterprise?
Costs vary depending on scale, platform (public vs private), and integrations. Most enterprises begin with a modular or pilot solution to validate ROI before scaling. The biggest savings come later — by reducing intermediaries, paperwork, compliance effort, and fraud exposure.
4. Can blockchain integrate with existing ERP or CRM systems?
Yes. Enterprise-grade platforms like Hyperledger Fabric and R3 Corda are built to integrate with ERP, CRM, and supply chain software using APIs. Blockchain doesn’t replace existing systems — it enhances them with transparency and automation.
5. What is the biggest barrier to blockchain adoption in enterprises today?
Technology is not the barrier — change management is. Most organizations need internal alignment, training, and executive sponsorship before adoption. Once teams understand the operational and compliance benefits, adoption accelerates quickly.






Recent Comments