The Future of Smart Homes with IoT Integration
The Future of Smart Homes with IoT Integration
Smart homes with IoT integration are revolutionizing the way people live in 2025 — far beyond remote-controlled lighting and voice-activated speakers, they represent a new era of intelligent, connected living. They represent a new era of intelligent living — where AI, edge computing, and data analytics converge to create connected ecosystems that think, learn, and respond to human behavior.
From energy efficiency to predictive maintenance, IoT is redefining the way we interact with our living spaces — transforming homes into intuitive environments that deliver comfort, security, and sustainability.
Why Smart Homes with IoT Integration Matter in 2025
In 2025, the global smart home market is projected to surpass $180 billion, fueled by advancements in IoT, AI, and edge computing. Consumers now expect more than voice-controlled lights — they want holistic, data-driven living experiences that improve efficiency and personalization.
IoT integration allows devices to share data through a common network, enabling real-time insights and adaptive automation. For example, thermostats learn your schedule, refrigerators track food expiration, and security cameras alert you before suspicious activity occurs.
This integration transforms everyday living by making homes more energy-efficient, secure, and responsive to individual lifestyles.
How Smart Homes with IoT Integration Shape Modern Living
1. Interconnectivity and Automation
IoT-enabled devices connect through central hubs or cloud-based ecosystems like Google Home, Amazon Alexa, or Apple HomeKit. These systems allow homeowners to automate daily routines — from setting morning lights to locking doors at night — without manual effort.
Through edge computing, data processing now happens locally within smart devices, reducing latency and increasing reliability. This means your home can respond instantly to commands, even when offline.
2. AI-Driven Personalization
AI complements IoT by analyzing behavioral patterns to create personalized experiences. Smart speakers learn your preferred music genres, while HVAC systems predict ideal room temperatures based on historical data.
Predictive intelligence allows your home to adapt proactively — for instance, preparing your coffee when it detects your alarm has gone off or adjusting lighting as natural sunlight changes throughout the day.
3. Real-Time Data for Enhanced Control
Real-time data streaming is the backbone of IoT-integrated smart homes. Through smartphone dashboards or wearable interfaces, homeowners gain 24/7 visibility into energy consumption, appliance performance, and security alerts.
This connectivity empowers users to make data-backed decisions — like adjusting power usage or identifying faulty devices — improving both sustainability and cost efficiency.
Core Benefits of Smart Homes with IoT Integration
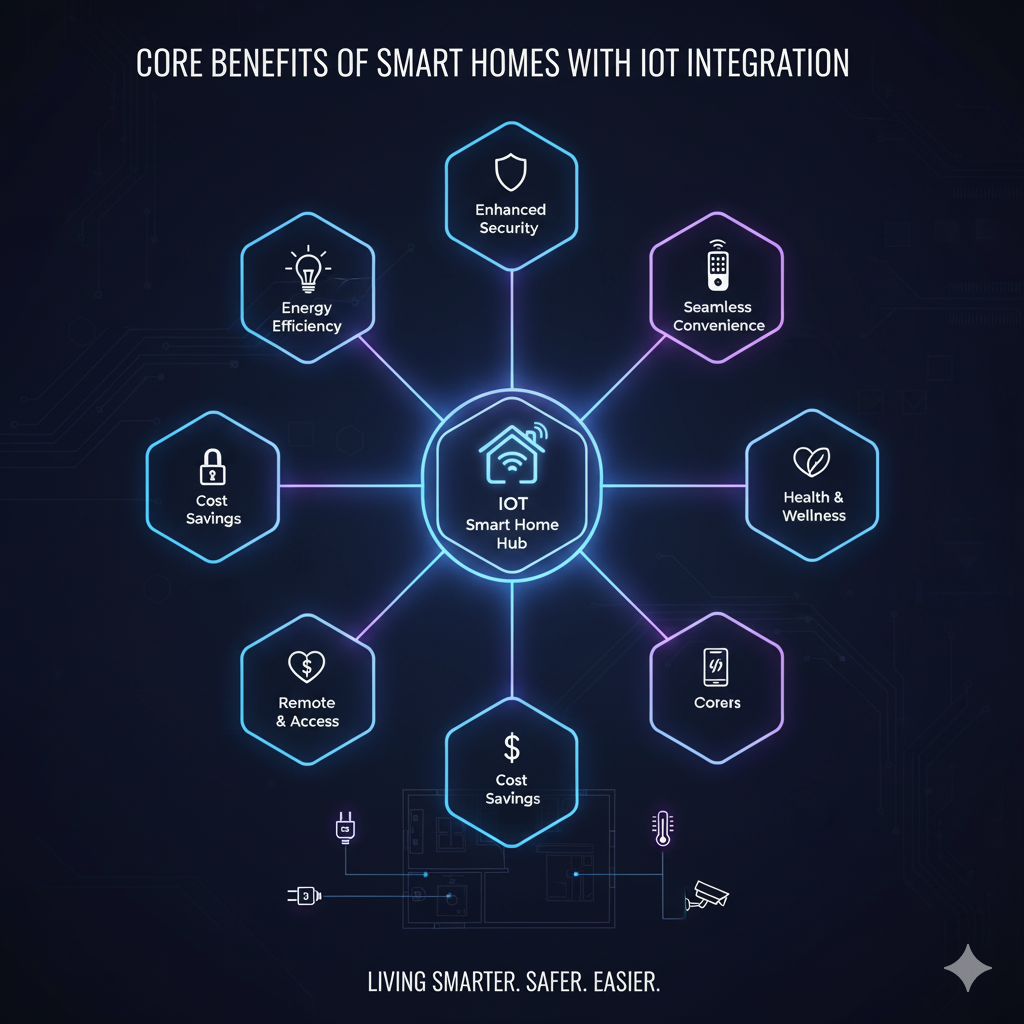
1. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
IoT-enabled smart homes reduce energy consumption by using sensors and automation to optimize electricity usage. Smart thermostats such as Nest or Ecobee automatically regulate heating and cooling, leading to up to 25% lower utility bills.
Integration with renewable energy systems, such as solar panels and smart meters, ensures that energy is used intelligently — storing excess power and drawing from the grid only when necessary.
2. Security and Privacy Enhancements
IoT-based security systems combine cameras, motion detectors, and door sensors to create real-time, AI-driven surveillance. Modern systems like Ring and Arlo can differentiate between humans, pets, and vehicles, reducing false alarms.
Biometric authentication, blockchain-backed device IDs, and encrypted communication protocols are emerging as key tools to prevent hacking and unauthorized access.
3. Improved Accessibility and Quality of Life
IoT devices empower individuals with disabilities or mobility challenges to control their environment through voice commands or gesture recognition. From automated blinds to adaptive lighting, homes are becoming more inclusive and responsive to individual needs.
4. Predictive Maintenance and Cost Savings
IoT sensors continuously monitor the performance of household systems. If your water heater or HVAC unit starts showing anomalies, predictive analytics can alert you before a costly breakdown occurs.
This predictive maintenance capability extends appliance life and reduces unplanned service costs.
Core Technologies Behind Smart Home IoT Integration
1. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI enables devices to learn from user behavior, while ML algorithms improve system performance over time. These technologies help automate decision-making and tailor responses to each household’s unique usage pattern.
2. Edge Computing
Processing data closer to the source (on the device) minimizes delay and bandwidth usage. Edge computing ensures that smart home systems function smoothly even with intermittent internet connectivity.
3. 5G and Wi-Fi 6 Connectivity
High-speed connectivity through 5G and Wi-Fi 6 provides the bandwidth required for multiple IoT devices to operate simultaneously without lag — from security cameras to smart entertainment systems.
4. Interoperability Standards
Protocols such as Matter, Zigbee, and Z-Wave are enabling seamless interoperability between devices from different manufacturers — a major step toward creating unified smart home ecosystems.
Smart Home Applications: Real-World Examples of IoT Integration
1. Intelligent Energy Management
Companies like Tesla and Siemens are developing energy management systems that use IoT to balance consumption, generation, and storage. Smart homes can automatically shift to stored solar energy during peak hours, reducing costs and carbon emissions.
2. Smart Kitchens and Connected Appliances
IoT-connected appliances are making kitchens more efficient. Refrigerators can suggest recipes based on available ingredients, ovens can preheat remotely, and dishwashers can optimize water usage.
3. Advanced Home Security Systems
IoT-driven cameras and sensors create a connected security network that provides real-time alerts, facial recognition, and cloud-based video storage. Some even integrate with local authorities for emergency notifications.
4. Health and Wellness Monitoring
Wearables and IoT-integrated health devices track vitals like heart rate, sleep, and movement patterns, allowing homes to adapt for occupant well-being. For instance, air purifiers activate automatically when pollution levels rise indoors.
Challenges and Considerations in IoT-Integrated Smart Homes
1. Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Risks
As the number of connected devices grows, so does the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. Businesses must adopt end-to-end encryption and blockchain-based authentication to secure user data.
2. Device Compatibility and Integration Gaps
Many homeowners face issues when integrating products from different brands. Adoption of open standards like Matter helps bridge this gap, ensuring compatibility across ecosystems.
3. Cost and Scalability Concerns
While the initial investment in IoT devices can be high, the long-term savings from automation and energy efficiency make smart homes a worthwhile investment. Scalability remains a challenge, but cloud-based solutions are helping make IoT accessible to more users.
Ethical and Environmental Considerations
With IoT data being continuously collected, ethical data governance becomes crucial. Businesses must ensure transparency regarding how user data is stored, processed, and shared.
On the environmental side, IoT-driven energy management contributes significantly to sustainability goals, aligning with global initiatives like the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
What the Future Holds for Smart Homes with IoT Integration
The next evolution of smart homes with IoT integration will blend AI, 5G, and edge computing to create homes that anticipate and act without explicit commands. We’ll see autonomous decision-making — for example, homes negotiating energy prices directly with utility providers or adjusting environments for health optimization.
Additionally, digital twins (virtual replicas of physical homes) will allow predictive maintenance and simulation of design changes before implementation.
By 2030, smart homes will transition from being luxury conveniences to essential, connected ecosystems that shape sustainable urban living.
Implementation Roadmap for Businesses Entering the Smart Home IoT Market
- Identify Business Value — Define clear goals, such as reducing energy waste or improving user convenience.
- Select the Right Platform — Choose an interoperable IoT ecosystem supporting open standards.
- Ensure Robust Security — Implement multi-factor authentication, encryption, and firmware updates.
- Integrate AI and Data Analytics — Leverage real-time data to personalize and optimize performance.
- Measure ROI and User Experience — Track customer satisfaction, cost reduction, and sustainability metrics.
Transform Everyday Living with Tiso Studio
Explore how Tiso Studio’s Emerging Technology services help businesses design and integrate IoT-driven smart solutions for homes and enterprises.
FAQ’S
1. Are IoT-powered smart homes expensive to build and maintain?
Not necessarily. The initial setup cost can vary based on the level of automation, but long-term savings from energy efficiency, predictive maintenance, and reduced breakdown costs often offset the investment. Scalable device ecosystems also allow homeowners to start small and expand over time.
2. How safe is my personal data in a smart home ecosystem?
Modern smart homes use encryption, biometric authentication, and secure communication protocols to safeguard data. To strengthen security, devices using Matter, Zigbee, or Z-Wave standards ensure safer interoperability and firmware-level protection against hacking.
3. Can IoT smart homes function without internet connectivity?
Yes — with edge computing, many smart devices can operate and process data locally even when the internet is down. Core features like automation, lighting, and HVAC can still run offline, while cloud-based services resume once the connection is restored.
4. What industries are benefiting from smart home IoT beyond residential use?
IoT automation is now being scaled into hotels, eldercare facilities, commercial buildings, and smart city infrastructure. These industries use similar technology stacks for energy optimization, security monitoring, and predictive maintenance.
5. Will interoperability issues between different brands eventually disappear?
Yes — with emerging universal standards like Matter, smart home ecosystems are moving toward seamless cross-brand compatibility. This shift allows users to mix-and-match devices from multiple manufacturers without worrying about connectivity conflicts.






Recent Comments